If it seems like everyone has a smartphone these days, it’s because everyone does. Smartphone penetration rates around the globe are at an all-time high, and projections show 36% of the world’s population (4 billion people) will own at least one smartphone by 2020.
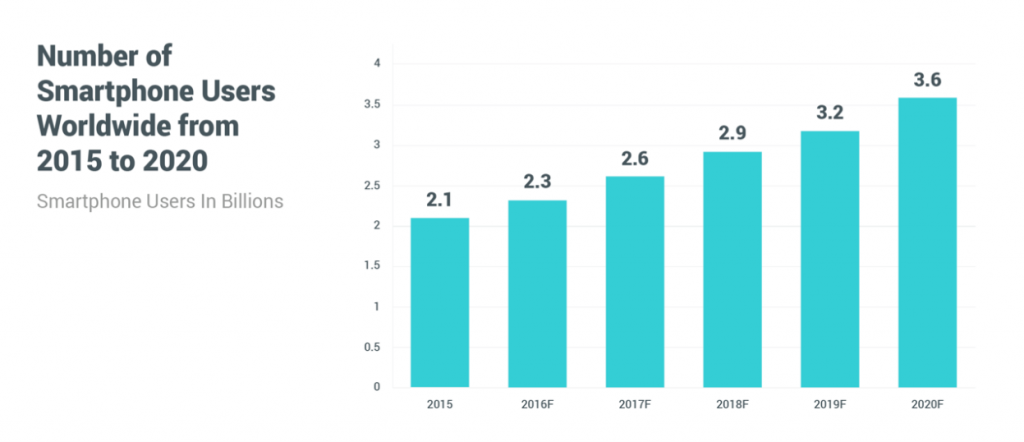
Despite the advanced technology found on the devices in our pockets, smartphones are next to useless without the ability to download and run applications. According to a Sensor Tower report, more than $86 billion was spent on app downloads in 2017 alone.
The number of global app downloads is only expected to grow, especially in emerging markets like India and China, where downloads have surpassed 215% growth over the past two years. This information is important because it establishes mobile apps as one the most influential and powerful global industries to date.
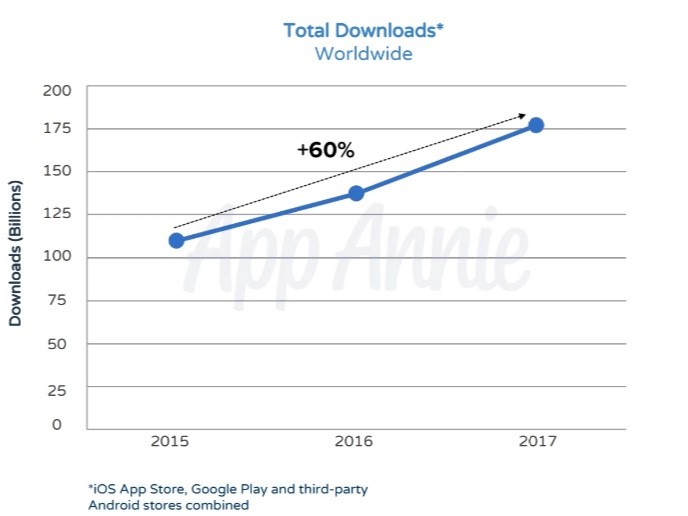
As global app revenue continues to rise and download numbers skyrocket, the global app economy is projected to change and shift substantially. In response to the projected change, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) and telecom carriers are into meeting related consumer demands and means to monetize them.
What is the App Economy?
Forecasts indicate that change to consumer demand is coming to the global app economy; but what exactly is the app economy, and how does it affect end users and developers? According to Techopedia, the app economy refers to,
“the range of economic activity surrounding mobile applications… encompassing the sale of apps, ad revenue or public relations generated by free apps and the hardware devices on which apps are designed to run.”
The value of the app economy is derived from consumer markets and enterprise applications. According to the State of the App Economy Report, as of 2018 the app economy is valued at $950.6 billion.
The app economy also includes 4.7 million developers, software engineers, system managers and teachers, accounting for more than 444,000 computing jobs in the United States alone.
What Trends are Affecting the App Economy?
Several trends converged in 2019 which are projected to have a significant impact on the app economy.
Stronger Focus on Customer Engagement
Customer engagement on mobile devices has changed significantly in the last 5 years. OEM’s and Telecom carriers have responded with a shift in app engagement strategies. Focused on generating a “lifestyle experience,” OEMs and telecom carriers are developing markets that generate new revenue streams, eliminating their commitment to markets that are no longer profitable.
One such market is the gaming category, which have experienced a sharp decline in popularity and has been mostly absent from the “Top 5 Grossing” app positions for the last year. Video is now the dominant form of content streamed to mobile devices.
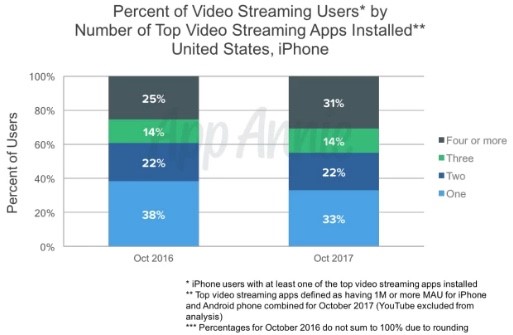
App Store Saturation
The app store is a direct-access marketplace that connects app users and app developers. The app store is critically important to the global app economy because it enables developers with a marketplace where they can engage with users directly, without interference from manufacturers of mobile devices, otherwise known as OEMs.
However, as the number of smartphone users continues to grow, app stores are becoming oversaturated. Despite the growing number of app downloads, developers are struggling to distinguish their apps from the rest of the pack.
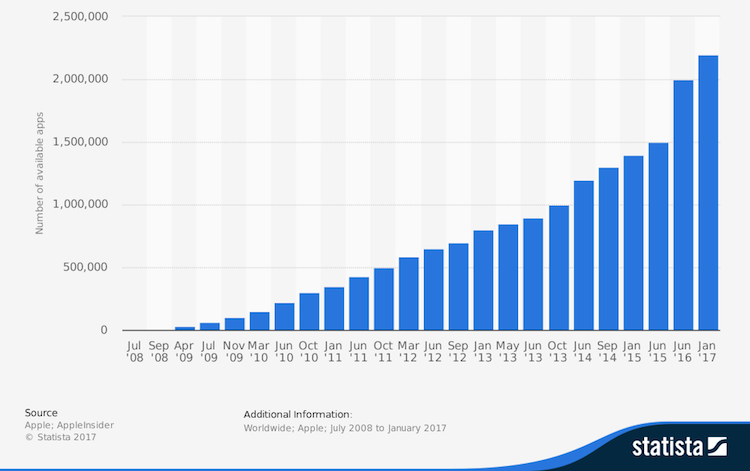
According to mobile app marketing trends, there is now a combined 10 million apps available to consumers between the various app stores. As a result many app developers are flocking to smaller app stores like Amazon Appstore, GetJar and Appolicious as alternative channels to reach new users. OEM app stores also emerge as alternative with leading players such as Samsung and Xiaomi that accelerate their efforts to become a more dominant player in app economy, attracting growing number of apps.
However, the shift in strategy may be too late when you consider historically spotty mobile service in emerging markets. Combined with the rise of streaming video, the explosive growth of mobile advertising and the saturation of the app economy – A situation develops in which the app store’s function has largely changed.

Trends suggest a marketplace dominated by a small number of successful apps who have effectively secured the entire market for themselves. Apps like Facebook, Lyft and Amazon continually grow their audience via the different app stores, but few users are likely discovering those apps for the first time.
Instead, we find an app store that functions like an archive, where in users already know which apps they would like to download.
What is the Role of OEMs in the App Economy?
The top OEMs (original equipment manufacturers) for mobile devices are Samsung, Huawei, and Apple, closely followed by global brands like Oppo, Vivo, Xiaomi, Lenovo/Motorola and LG. OEMs are critical to the app economy, playing a significant role in determining how, when and why mobile devices are used.
Prior to the development of the app store, OEMs played a larger role in determining which apps were pre-installed on their devices, and which apps could or could not be downloaded by the user. As mentioned, some OEMs also promote their own app stores, yet generally experiencing has limited success due to various reasons: Limited app offering, low attractiveness for developers, lack of domain expertise, etc.
How is That Role Expected to Change?
The ultimate decision as to what apps will be downloaded to a device may be influenced by OEMs (e.g. pre-install), however research suggests consumers are becoming more and more picky in how they search for apps on their mobile devices.
OEM’s are adapting to the oversaturated app economy by distributing their new technology directly into the hands of their users.
Peer-to-Peer App Sharing
Peer-to-peer app sharing platforms are on path to outpace app stores as the new form of discovery, especially in markets with limited internet availability.
According to Rajeev Dhal , Vice President of SHAREit India, “this form of app discovery has its intrinsic benefits over inorganic downloads and it is now touching millions of users across all continents.”
It offers very high engagement and retention rates and provides users in emerging markets to apps that were previously inaccessible thanks to poor network connectivity and lack of data service.
Slow data speed continues to prevent even higher growth rates in emerging markets where the majority of the population lives in rural areas without data connections. App developers looking to penetrate the BRIC app economy should focus on apps that don’t require large data usage to download or use, and enable offline access whenever possible.
Wearable & In-Home Devices
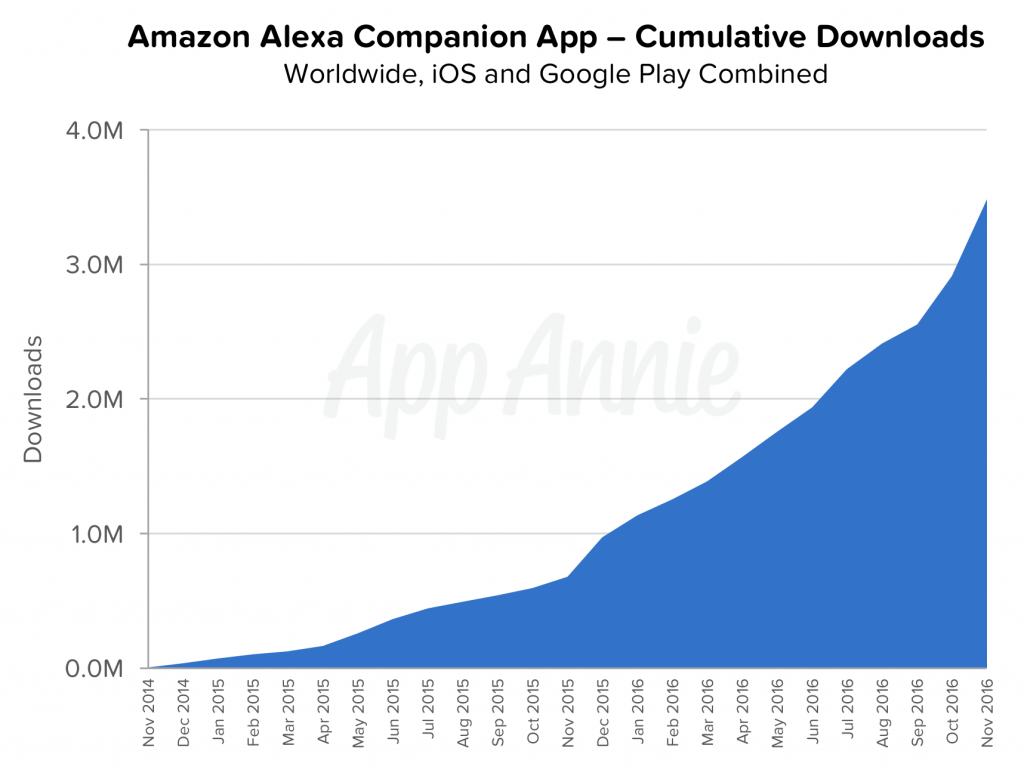
OEMs will shift investments to wearables and in-home devices. The App Economy will likewise adopt the associated companion apps like Amazon’s Alexa, which was downloaded approximately 3.5 million times between iOS and Google Play, according to AppAnnie.
What is the Role of Carriers in the App Economy?
As previously mentioned, OEMs play a significant role in determining how, when and why mobile devices are used. However, where smartphones are used is ultimately determined by the availability of data and internet service.
Mobile carriers have been largely successful in expanding their networks to emerging markets where a rise of smartphone ownership has increased consumer demand for faster download speeds and better mobile coverage.
How is That Role Expected to Change?
4G access enabled users to join the online community in larger numbers, and telecom industry reports show consumer-driven data consumption at an all-time high.
Greater access comes with greater demand for faster mobile service, especially in emerging markets like China, India, Brazil and Russia where consumer spending has more than doubled in the past two years.
2020 is the year that consumers and governments have demand greater deployment of 5G networks from mobile carriers. Thus, the role of mobile carriers in the app economy is likely to change in the coming years as 5G offers opens up an array of new opportunities powered by extended communications capabilities that were never before available.
Mobile Carriers Improve Data Service
Faced with an unprecedented demand for greater access and capabilities, telecom mobile carriers have eagerly pursued the development of 5G service. 5G powered apps were introduced last year and carriers have promised widespread 5G coverage by late 2020.
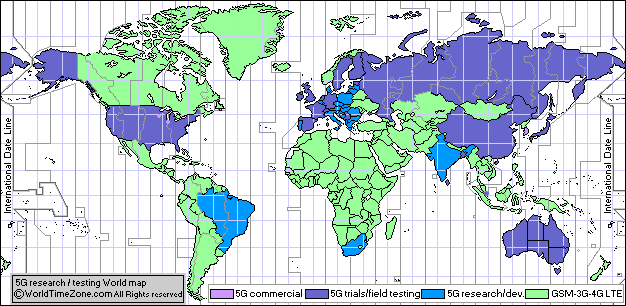
Download speed is projected to increase up to 100x faster than 4G, which will increase the capabilities of new apps, significantly expanding mobile app economy. One area where consumers are likely to see the results is 3D gaming, VR and augmented reality.
Strength of the Mobile App Economy
Change is on the horizon for OEMs, mobile carriers and the app store itself. The app economy remains as strong as ever and if current trends are to be believed, consumer demand will grow and open up new revenue opportunities for OEMs and telecom carriers.
As recently released by Appnext, it works hand in hand with multiple mobile carriers and operators globally, including several of the top 10 leading OEMs globally. Appnext offers those with variety of flexible app discovery integrations customized to each OEM’s strategy and evolves its offering as OEMs and carriers take a greater role in the app economy.




Comments are closed.